Emergency Nursing as discussed by Sir Tom Labonete RN-EMT, LPT, Italian Model, Rockstar on 12-01-2024
Emergency Principles
- Common sense: a lot of individuals feel pressure and anxiety at the scene. Attempt to maintain the intuition held by an emergency responder. Do not forget the basic principles.
- Calmness and Patience: maintain a calm demeanor. Patients can pick up feelings of anxiety especially if displayed by the emergency responder.
- The 90-5-5 Principle: 90% of the focus of the emergency response is delegated to the safety of the responder. 5% is for the patient, and 5% is for the bystanders. There is no point in rescuing a victim if the responder themself is put in danger, and may become a victim as well.
- Body Substance Isolation, Handwashing: always minimize the potential for contamination.
- Do not treat at the site. The site of danger is almost never a safe place to perform treatment at. Attempt to make a distance of 50 meters or 100 paces.
- Rescue the patient first. This is a prerequisite for treatment, as mentioned in the previous principle.
- CHANT Method: when asking for help, include the:
- (a) Case, the accident or disaster being reported with the pertinent details of victim count, etc.
- (b) Help, expected required responses e.g. the need for fire trucks, a bomb squad, multiple ambulances
- (c) Address: the location as specific as possible, or important landmarks.
- (d) Name: name of the caller.
- (e) Telephone: the number of the caller for follow-up calls.
- Assess dysfunction related to the injury: the affected body parts are
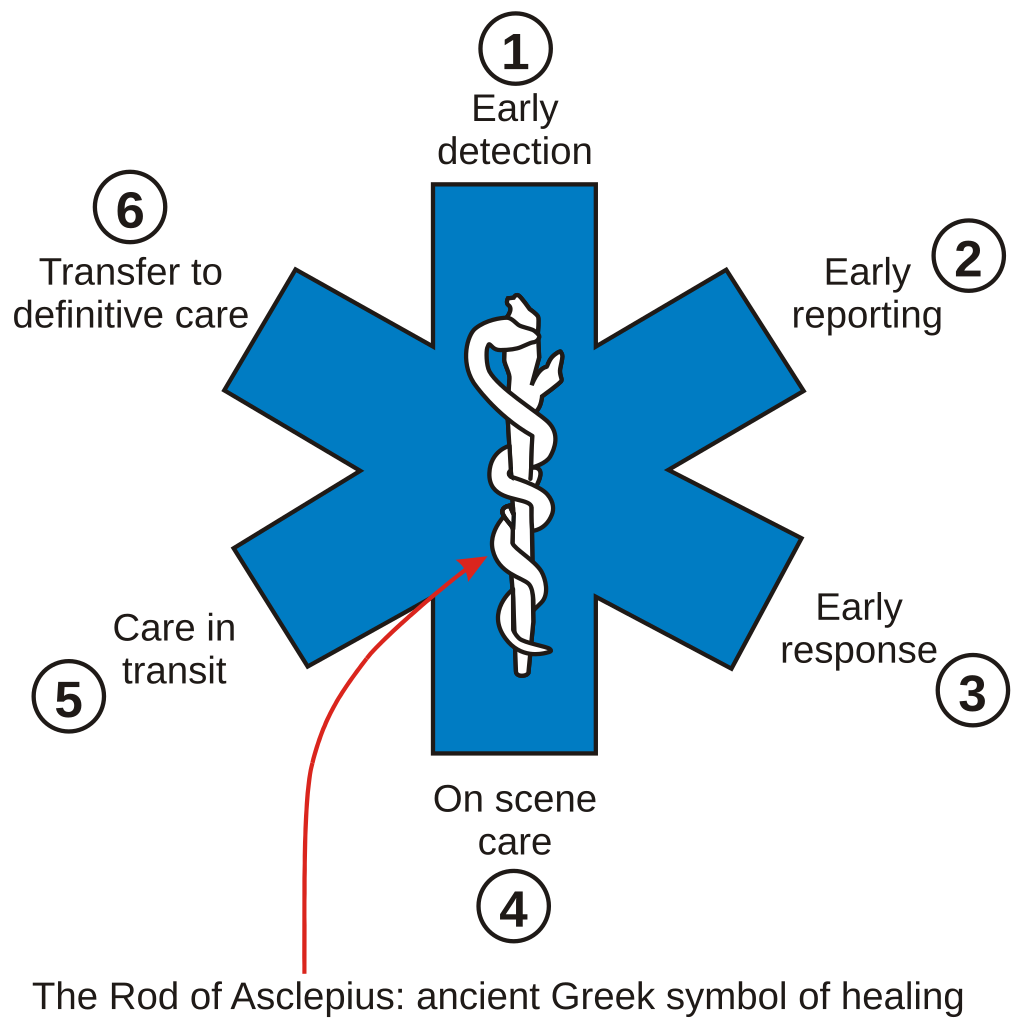
Star of Life
The Star of Life is a universal symbol for medical identification of emergency and first aid personnel. Specifically, its symbolism represents the six main tasks executed by rescuers all through the emergency chain.
- Early Detection: the use of the senses to determine the presence of an emergency or potential hazard.
- Early Reporting: calling for professional help with the CHANT method; dispatch is connected with victims.
- Early Response: if appropriate, the initiation of first aid response and immediate care to the extent of the first rescuers’ capabilities.
- On-scene Care: care provided by the EMS personnel arriving at the scene.
- Care in Transit: transportation of the patient to a hospital for specialized care. Medical care is given during transportation, especially for the ABCs of life.
- Transfer to Definitive Care: appropriate specialized care is provided at the hospital.
ABCDE
ABC is done within a hospital setting. The use of ABCDE is done outside of the hospital. The inclusions include deformity/disability and exposure/environment
Ambulance
The following are must-knows about ambulances and their operation.
- Driver: the driver must not leave the ambulance. They must be ready to initiate transport at a moment’s notice.
- Beacons: the beacon is a marker. These are the lights, sirens, and text of an ambulance that marks the presence and location of an ambulance.
- Patient Position: the patient is placed on a backboard and secured with spider straps. When applied with a c-lock and (head strap thing), it becomes a spine board.
- Number of Crew: the standard team is composed of one driver and two crew members.
Ambulances are categorized between two types:
- Type I: ambulances capable of providing Basic Life Support (BLS). This involves CPR, bandaging, wound management, oxygen delivery via cannula.
- Type II: ambulances capable of providing Advanced Life Support (ALS). This includes tracheostomies, intubations, and other invasive procedures.
Bone Injuries
These take the form of dislocations, the removal of a joint from its anatomical position, and fractures, the breakage of the continuity of a bone.
Nursing Considerations
- Immobilize the injury. Do not re-place or stretch the bone. Treat the fracture the way you found the fracture.
- Use an ice pack: cold therapy reduces swelling by inducing vasoconstriction.
- Pulse, motor, and sensory assessment before and after splinting. The presence of a pulse indicates that vascular damage is not present. Pulse is checked distal to the injury. Motor ability is checked by asking the patient to move the digits distal to the injury, and sensory assessment is done by checking for sensation.
- Splinting: the placement of an immobilizing object; anything hard enough to support an injury.
- Joint fracture: bandage from bone-to-bone proximal and distal to the injury.
- Bone fracture: bandage from joint-to-joint proximal and distal to the injury.
Hypothermia
| Degree | Manifestations | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | Shivering reflex | Warm the patient with warm food and fluids. |
| Moderate | No shivering, the hypothalamus fails to induce the shivering reflex. | Hypothermia blanket, as food may be aspirated. |
| Severe | Seizures | Seizure precautions for safety (side-lying), and hypothermia blanket, food may still be aspirated. |
| Profound | Dead or Dying | Transport to the nearest hospital. |
Frostbite
Localized destruction of tissue due to freezing temperatures. The most common areas to be frostbitten are the ears, nose, lips, fingers, and toes. This results in tissue taking a waxy appearance (white/pale yellow) initially before becoming blackened and necrotic (dry gangrene) if unmanaged. The nurse’s management is to soak the frostbitten tissue in warm water until the tissue appears pink or red.
Fainting
Fainting is caused by a temporary loss of blood in the brain. This may be caused by:
- Excitement: extreme excitement can cause fainting. This involves both positive and negative emotions.
- Lack of rest
- Extremes of temperature: vasoconstriction and vasodilation will reduce blood flow to the brain.
- Lack of sustenance (eating)
Warning Signs of Fainting
The warning signs of fainting includes nausea, dizziness, turning pale, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), blurry vision or tunnel vision, sudden feelings of warm and sweat, and feeling faint or light-headed.
Management
- Alert, Verbal, Pain, and Unresponsive (AVPU) and Level of Consciousness (LOC):
- Check for consciousness (alertness) by asking the patient if they are able to hear the patient.
- Next, check response to verbal commands by asking the patient to squeeze the fingers by asking the patient to do so.
- Induce pain (noxious stimuli) on the breastbone, traps, or (muscle between the thumb and index) to attempt to incite a response.
- If the face is red, raise the head to allow blood to circulate away from the head.
- If the face is pale, raise the tail to allow blood to circulate to the head.
- Place the patient on supine if necessary. This equalizes blood pressure and promotes blood flow to the head.
Bee Stings
Bees are normally peaceful insects that can become aggressive upon agitation of the bee hive or queen bee. They sting their pray at the cost of their own life as the stinger, parts of the digestive tract, muscles, and nerves are left behind after they sting their pray. Pain, swelling, allergy, or even anaphylaxis may occur.
Management
Initially after the sting, management is:
- Swipe with a card to safely remove the stinger embedded within the skin. Do not press or pull on the stinger.
- Wash the site to clean the puncture site and reduce risk for infection.
- Monitor the airway in case of an anaphylactic reaction that constricts the airway. The patient experiences heat and rashes due to an allergic reaction.
Within minutes,
- Obtain curved tweezers to remove the stinger if the initial removal with a card is not done. The tweezers are curved avoid squeezing the end of the stinger where toxins may reside.
Burns
Fire is dangerous because of its heat and the toxic fumes produced by burning materials. For a fire to form, the fire triad (or tetrahedron) is required:
- Heat: sufficient heat is required for a heat to sustain its chain reaction.
- Oxygen: oxygen is essential for the chemical reaction of a fire. Oxygen is a flammable gas.
- Fuel: fuel is continuously consumed in fire
- Chain Reaction/Combustion
Objectives
- RACE/ARCE: RACE is used when patients are inside a burning room, as rescue is more urgent than sounding the alarm.
- Alarm: (2:14) sound the alarm; fire alarm if present, or call for help if relevant.
- Rescue: rescue any persons or patients in the vicinity.
- Contain/Confine: remove fuel from the room if possible (burnable objects) and close doors to burning rooms, if possible.
- Extinguish/Evacuate: use a fire extinguisher if present and/or evacuate the building.
- Airway: many burn injuries are related to inhalation of toxic gases or burning of the airway, inside or out.
- Never Remove Clothes: burning clothes may adhere to the skin, and its removal may cause the skin to also be removed.
- Three Magic Words: Stop, Drop, Roll
- Medication via IV: burns will impair gastrointestinal functioning, making oral medications ineffective.
Therapeutic Goal
- ABCs of Life (as usual)
- LRS via IV: the infusion of Lactate Ringer’s Solution using Parkland’s Formula.
Parkland's Formula
This is given to replace fluid and electrolyte loss from burns from leakage and from direct loss within the first 24 hours. In infusion,
- The first 50% of fluids to infuse is completed within 8 hours,
- the following 25% is infused in 8 hours,
- the final 25% is also infused in 8 hours.
- Analgesia: as pain is difficult
- Antibiotics: due to the risk for infection
- Temperature: to determine the presence of a fever
- Monitor Weight: to monitor fluid status
Burn Rhabdomyolosis
A burn patient will have muscle breakdown. This may be excreted in the urine, giving it a bright red appearance, which is a good outcome. This signifies that the kidney is excreting waste, which includes breakdown products of muscle. In other cases, this may also be another cause of complication in patients, such as in kidney failure.
Poisoning
| Corrosive Poisoning | Non-corrosive Poisoning |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify the poison | 1. Identify the poison |
| 2. Do NOT induce vomiting | 2. Induce vomiting |
| 3. Position on the left side | 3. Position on the left side |
| 4. Transport the patient | 4. Transport the patient |
Management
A nasogastric tube is used to perform gastric lavage.
Jellyfish Stings
Jellyfish stings can cause rapid death in large doses in some species of jellyfish, or only pain. It also varies in the number of stingers that comes in contact with an individual.
Management
- Pour sea water on the sting rather than freshwater and urine.
- Scrape the tentacles using a card (remember bee stings?)
- Vinegar/Baking Soda
- Calamine Lotion: anti-pruritic lotion
- Transport the patient
Snake Bites
The intervention is to, first, assess the bite mark. Afterwards, wash the site and keep the patient still to reduce the spread of venom, if present. Do NOT use a tourniquet, as this often causes more harm than good, as the venom forms potential boluses that are released upon the release of the tourniquet.
Tourniquet
Tourniquets are only good for two hours. These are used for amputations and severe bleeding only.
| Venomous | Non-Venomous | |
|---|---|---|
| Bite Mark | Fangs | Multiple teeth |
| Eyes | Oval/Slit-eyed | Round |
| Head | Triangular | Round |
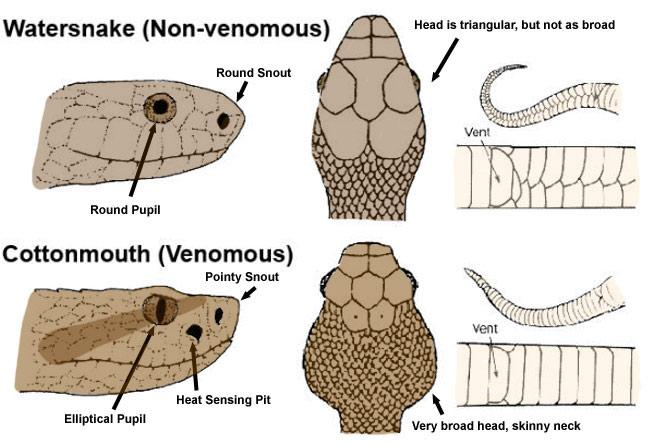 |
Management
Management is symptomatic. Different toxins present different symptoms, causing pain, affecting the heart, clotting the blood, etc. These symptoms are managed as they appear. The only actual treatment for the venom is an antitoxin from the specific snake venom.
- Chemotoxic: destruction of tissue
- Hemotoxic: causes coagulopathies
- Cardiotoxic: affects heart functioning
- Neurotoxic: causes extreme pain
Q&A
EMT responsibility:
- Find and manage emergencies
- Recognize and eliminate emergencies
- Recognize and familiarize with emergencies
Rationalization
1
An emergency cannot be “eliminated” nor familiarized with; each emergency is unique and the EMT must assess the environment and details of the emergency. The EMT uses all five senses to detect an emergency.
Basic requirement before performing first aid:
- Training
- Medical background
- Common sense
Rationalization
3
A medical background is not necessary. Training is done before you even get placed at a scene where you are about to provide first aid.
In an ambulance,
- You can load via GCash
- You can load a dead body
- You can load a dying patient
Rationalization
3
Maybe some ambulances accept GCash as payment now.
The most common type of prehospital injury:
- Heart attack
- Bleeding
- Ghosting by a boyfriend
- Infection
Rationalization
2
Bleeding (trauma) is the most common type of prehospital injury.
In an motor vehicular collision, who is more likely to survive?
- A driver struck at the front of the car
- A driver struck at the door
- A car hit from above by a boulder
Rationalization
2
A car hit from the front will have a sufficient crumple zone and air bag protection to reduce the risk of injury.
Who are seated in the front of the ambulance?
- Driver and Witness
- Driver and Patient
- Driver and 2 EMT
- Driver and 1 EMT
Rationalization
4
No ratio
Who is less likely to survive?
- A driver struck at the door
- A driver struck at the front of the car
Rationalization
1
No ratio
What does the latin term “primos auxilium” stand for?
- Primary Survey
- Prime Axillary
- First Aid
Rationalization
3
No ratio
In the safety ratio, what does 90% of the rescuer’s focus get dedicated to?
- Victim
- Bystanders
- Rescuer
Rationalization
3
In the safety ratio, 90-5-5, the rescuer prioritizes their own safety (90%), then the victim (5%), then the bystanders (5%).
In the 2005 AHA update, how are the ABCs of life organized?
- CAB
- BAC
- ABC
- CBA
Rationalization
3
In 2005, the ABCs of life were as they are now; alphabetical. Airway is established first, then breathing, then circulation. This changes in 2010, when circulation became prioritized over airway and breathing— CAB.
The French term “cravat” is synonymous to:
- Croissant
- Cadaver
- Neckerchief
Rationalization
3
No ratio
What is the meaning of “hyphema”?
- Bleeding in the Nose
- Bleeding in the Ears
- Bleeding in the Eyes
Rationalization
3
No ratio
A vehicle that will extinguish fire and is being operated by fire fighters is called:
- Fire Hydrant
- Penetrator
- Fire Truck
- Fire Engine
Rationalization
4
The fire engine is the fire-fighting part of a firetruck that carries and pumps water. The fire truck is designed to carry ladders, rescue equipment, and other special fire fighting equipment.
What does ABCDE stand for?
- Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Deformity, Exposure
- Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disaster, Emergency
- Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Danger, Environment
Rationalization
1
DE stands for Deformity and Exposure.
Philippine Red Cross is a:
- Public Organization
- Private Organization
- Government Agency
- Branch of the Department of Health
Rationalization
2
The PRC is a private, non-profit humanitarian organization.
The antidote for spinal anesthesia is:
- Morphine
- Nitroglycerin
- Epinephrine
- Caffeine
Rationalization
3
Spinal anesthesia is a downer. Morphine is a downer. Nitroglycerin causes vasodilation, and would further decrease blood pressure. Caffeine is a stimulant, but is not appropriate.
A late symptom of compartment syndrome is:
- Pedal Edema
- Paresthesia
- Paralysis
- Pain
Rationalization
3
Paralysis is a late, perhaps the latest manifestation of compartment syndrome. This is part of neurovascular impairment, and occurs due to a lack of blood flow to the affected extremity.
A patient with hyphema is first assessed for:
- Stroke
- Vision
- Pain
- Movement of the eyeball
Rationalization
2
Always assess the functionality of the injured body part first.
An ambulance going to an impact site utilizes:
- Sirens only
- Lights only
- Lights and sirens
Rationalization
3
Full lights and sirens are used when heading to a scene. This permits the emergency vehicle to counterflow and to be a priority on the road.
A patient is loaded into the ambulance:
- Love first
- Head first
- Injured part first
- Feet first
Rationalization
2
No ratio
Rescuer attire is colored:
- Green
- Pink
- Blue
- Orange
Rationalization
4
Orange strips that are highly visible are found in EMT attire, allowing for visibility even at night. Green attires are for Grab drivers. Pink attires are for FoodPanda drivers. Blue attires are for?
Rationalization
Angkas drivers
A patient on an ambulance stretcher/gurney going down the stairs is transported:
- Stretcher first followed by the patient
- Feet first
- Head first
Rationalization
2
The patient is kept as level as possible, and the feet are taken down the stairs first.
The RN inserts an IV NSS inside a Type I ambulance. Is this appropriate?
- Yes, in any scenario
- Yes, unless the vehicle is moving
- No
Rationalization
3
A Type I ambulance is only able to provide Basic Life Support (BLS). No invasive procedures, even for intravenous access, is done in a Type I ambulance.
Paralysis in the later stages of compartment syndrome is caused by:
- Inflammation
- Lack of blood
- Bone damage
- Pain
Rationalization
2
Prolonged unmanaged compartment syndrome begins with pain and ends in paralysis. These are signs of neurovascular impairment, which involves a loss of blood supply.
Which are two important rescue contents of a fire engine?
- Axe and ladder
- Hose and ladder
- Hose and water
Rationalization
1
Rescue contents include the axe and ladder. The hose and water for fire-fighting, rather than for rescuing.
If the patient has no heartbeat:
- Love the patient
- Check for responsiveness
- Perform CPR
- Perform defibrillation
Rationalization
3
Responsiveness should have already been checked prior to checking for a pulse. Defibrillation is never done for a patient with no pulse. Loving the patient is nice, but it probably won’t start their heart.
In the CHANT mnemonic, what does H stand for?
- Help
- Handicapped
- Harm
- Hypothermia
Rationalization
1
H stands for Help. The CHANT mnemonic is used for reporting emergencies to the authorities: Case (nature of emergency), Help (expected required help), Address (location as accurate as possible; landmarks if present), Name, and Telephone Number.
In the 2010 AHA update, how are the ABCs prioritized?
- BAC
- ABC
- CBA
- CAB
Rationalization
4
As of 2010, the American Heart Association has given priority to Circulation before the Airway and Breathing. This is because the blood may still contain oxygen that can be utilized even as the patient is unable to breathe, allowing it to provide some level of sustenance to the brain and other tissues.
In mild hypothermia, what is the nurse to give?
- Jacket
- Hot chocolate
- Epinephrine
- Blanket
Rationalization
2
Warm food and fluid is given for patients with mild hypothermia, manifested by shivering.
In a sprain, what tissue is broken?
- Muscle
- Promises
- Ligaments
- Tendon
Rationalization
3
Muscles and tendons are damaged in strains. Promises are made to be broken.
How does a monophasic defibrillator work?
- Sends an impulse to all nerves of the body
- Sends an impulse to the brain
- Sends an impulse from the ventricles to the atria then atria to the ventricles
- Sends an impulse from the ventricles to the atria
Rationalization
4
No ratio
In a hypothermic patient who is not shivering, the nurse gives:
- New clothes
- Blanket
- A hug
- Warm fluids
Rationalization
2
A blanket is given. New clothes is not indicated unless the patient’s clothes/body is wet. Warm fluids are given for mild hypothermia— patients who are shivering. Those who have lost the shivering reflex may be prone to aspiration if given warm fluids or food. A hug is nice, but wouldn’t be as effective as a blanket.
In a client with a gunshot wound to the chest, what intervention may be expected?
- Use of a portable x-ray
- Chest tube thoracotomy
- Anticoagulant therapy
- Tracheostomy
Rationalization
2
A gunshot wound to the chest places the patient at risk for pneumothorax and hemothorax. A chest-tube thoracotomy set is prepared in such a case.
A high-oxygen flames tend to emit what color glow?
- Red
- Yellow
- White
- Blue
Rationalization
4
No ratio
A patient who has been shot experiences what feeling?
- No sensation
- Warm sensation
- Wet sensation
- Cold sensation
Rationalization
2
Gunshot patients often report a warm feeling produced by a bullet. This is due to its velocity and contact with exploding gunpowder when it was shot.
In a search and rescue, the rescue team searches for:
- Retrieving a dead person
- Searching for high-value items
- Searching for a living person
Rationalization
3
No ratio
In a patient rescued from a frozen lake, all wet, conscious, the first intervention to keep him warm is:
- Undress the patient
- Give the client a cup of boiling water.
- Provide a blanket
- Load the patient inside the ambulance
Rationalization
1
Wet clothes will literally suck the warmth from the body. These must be removed immediately once the patient has been moved to a private, unexposed space such as within an ambulance.
A monophasic type defibrillator will deliver how many joules?
- 50V
- 110V
- 200J
- 360J
Rationalization
4
No ratio
What is more dangerous?
- Dropping a major subject in nursing
- Dropping a lit match on gasoline
- Dropping a lit cigarette on gasoline
Rationalization
2
While Option 1 is extremely dangerous, we must follow Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and prioritize Physiological Safety. Gasoline fumes are flammable, and can be lit by a lit match, but is unlikely to be lit by a cigarette.
An EMT’s most important must-have equipment is:
- Bandage
- Stethoscope
- Tourniquet
Rationalization
2
Bandages and tourniquets can be improvised with materials in the surroundings. A stethoscope cannot.
Is the hair a conductor of electricity?
- No
- Yes, but only when the hair is very dry
- Depends on if the patient is bald
- Yes
Rationalization
4
yes
An example of a superficial burn is a sunburn. This is also known as a:
- Micro burn
- Wind burn
- Flash burn
- Sunscreen burn
Rationalization
3
A sunburn is also known as a flash burn.
Upon arriving at the ER entrance, the personnel meeting the crew is the:
- Security officer
- Physician
- Nurse
- Orderly
Rationalization
1
The security officer takes charge in the entrance of the ambulance to outside the emergency department.
An injured individual who experiences multiple trauma feels cold before dying because of:
- Bradycardia
- Loss of Blood
- Delirium
- Weather
Rationalization
2
Blood loss is the cause of a cold sensation shortly prior to death in a patient who has experienced multiple trauma.
The PPE that can be used multiple times while attending to one patient is an:
- Gown
- Mask
- Eye shield
- Gloves
Rationalization
3
Gloves and gowns are replaced upon contamination, and masks are only good for 4 to 6 hours.
In the prehospital setting, who is more capable?
- All individuals are capable in an emergency
- A trained personnel
- A certified personnel
Rationalization
3
A certified personnel is someone who has been trained and tested. Not all individuals are capable, and some may even be obstructive or counterproductive.
The biphasic defibrillator delivers 200 joules in both directions.
- Its advantage is because of less risk for burn injury
- Its advantage is because of its higher success rate
- Its advantage is because of its lower current delivery
Rationalization
3
No ratio
While performing CPR, an earthquake occurs. The rescuer:
- Protects the patient
- Stops and hides
- Apologizes and leaves the patient
Rationalization
2
Remember that the nurse’s priority is themself if the scene becomes dangerous.
In gymnastics, a performer loses balance. What is the safest action to take?
- Tuck and roll
- Perform a sign of the cross
- Land on bended knees
Rationalization
1
Tucking and rolling distributes the force of landing across a larger area of the body, reducing impact force.
A patient enters the ER reporting domestic abuse. The nurse initially:
- Reports to the Head Nurse
- Reports to the Police
- Confirms with the family
- Refers the patient to a social worker
Rationalization
2
The case becomes medicolegal; the police must be involved first to collect the latest evidence available on the patient before treatment is initiated (unless urgent).
A patient is choking. First:
- Establish rapport
- Place the patient supine
- Ask the patient what object they are choking on
- Encourage coughing
Rationalization
4
Initially, have the patient attempt to expel the obstructive object by coughing.
IV Fluid needed in burn resuscitation:
- Whole Blood
- NSS
- D5050
- LRS
Rationalization
4
Lactate Ringer’s Solution (LRS) is used in fluid resuscitation as it contains essential electrolytes lost by burn patients, and as a buffer against metabolic acidosis (it is an alkylating agent).
Common Anatomical Airway Obstruction:
- Base of the tongue
- Saliva
- Dentures
- Tooth fillings
Rationalization
1
Keyword: anatomical; saliva is not a cause for airway obstruction. Dentures and tooth fillings are not anatomical obstructions.
A client reports to the ER after being stung by a bee. The first nursing action is to:
- Remove the patient’s rings in case of swelling
- Prepare an EpiPen
- Count the number of stings
- Open airway
Rationalization
4
ABCs of life. Also, because bee stings can cause anaphylaxis.
A patient is electrocuted after coming into contact to a live wire at a light switch. The priority is the:
- Patient
- Environment
- Light switch
- Finding help
Rationalization
3
A live wire at a light switch must be taken care of before assisting the patient, as touching the patient at this point can also electrocute the responder.
The patient becomes unconscious during the Heimlich maneuver. The nurse:
- Lies the patient down and performs ventilations
- Keeps the patient upright and continues the Heimlich maneuver
- Lies the patient down and performs CPR
Rationalization
3
The patient is laid down and CPR is performed. Ventilations are not done because of the obstruction in the airway. Ventilation may only lodge it further.
Who is the priority in the following cases?
- A classmate with no ballpen
- Elderly patient with chest pain
- Dehydrated infant
- Vomiting adult
Rationalization
3
The dehydrated infant will have the most greatly impaired circulation compared to an elderly patient with chest pain. A vomiting adult is not as urgent. A classmate with no ballpen is irresponsible.
A harmful substance that can be absorbed, inhaled, and ingested:
- Drugs
- Toxins
- Venom
- Poison
Rationalization
4
Substances that can be absorbed through the skin, inhaled, or ingested and cause damage are poisons. Venoms are injected through syringes or fangs. Toxins are an umbrella term for substances that cause harm and may refer to venoms.
Calling the authorities immediately if domestic abuse is suspected is done because:
- Patient’s latest memory of the incident must be documented.
- Fastest time to arrest the abuser
- The latest physical evidence must be collected
Rationalization
3
Physical evidence must be collected before they are lost or removed through treatment of the patient.
A bee sting occurs. The nurse prioritizes the:
- Card
- EpiPen
- Airway
- Killing the Bee
Rationalization
3
A bee sting may cause the airway to constrict in an anaphylactic reaction.
A patient with an inhalation injury must use a:
- Oxygen tent
- Nasal cannula
- Non-rebreather mask
Rationalization
3
The non-rebreather mask delivers the highest oxygen flow to a patient with an inhalation injury. Inhalation injury impairs air flow and gas exchange, and is an indication for high flow oxygen therapy.
What is more dangerous?
- Heat from an explosion
- Projectiles from an explosion
- Radiation burn from an explosion
Rationalization
2
Projectiles are more dangerous than heat from an explosion. Radiation (except infrared) is not usually a problem.
In ACLS, a patient with bradycardia can be given:
- Atropine
- Vicks Vapor Rub
- Amiodarone
- Diltiazem
Rationalization
1
Remember the two heart rate drugs: Atropine and Verapamil. Imagine the “A” in atropine as an upward arrow; a drug to increase heart rate, and the “V” in verapamil as a downward arrow; a drug to decrease heart rate.
Which is used in muscle cramps?
- Liniment
- Warm compress
- Cold compress
- Petrissage
Rationalization
2
A tense muscle is relaxed by a warm compress.
When is the usual onset of a thrombotic stroke?
- During exercise
- In the shower
- During their sleep
- During winter
Rationalization
3
Many individuals die from a thrombotic stroke that occurs during their sleep.
What is decontamination?
- Where patients proceed from exposed to unexposed
- Where patients proceed from dirty to clean
- When patients proceed from susceptible to immune
- When patients proceed from ill to healthy
Rationalization
2
Decontamination is the transition of a patient from dirty to clean.
Avoid giving oxygen masks to:
- Any children
- Patients with trisomy
- Patients with claustrophobia
- Pregnant patients
Rationalization
3
An oxygen mask can trigger feelings of claustrophobia. The remaining options are not contraindications for the use of an oxygen mask.
If an ambulance is heading towards you on the highway:
- The sirens sound low-pitched
- The sirens sound high-pitched
Rationalization
2
The pitch-shift of an incoming vehicle shifts its pitch higher because of the compression of soundwaves.
A patient with an exposed fracture must be:
- Treated for the bleeding first
- Given an anticoagulant first
- Treated for the fracture first
- Have their bones realigned first
Rationalization
1
Bleeding is the priority in an exposed fracture.
How many percent of the atmosphere is made up on oxygen?
- 21%
- 95%
- 5%
- 78%
Rationalization
1
No ratio
Common disorders of retired EMTs or rescuers include:
- Schizophrenia
- Depression
- Operational exhaustion
- Dementia
Rationalization
3
Operational exhaustion, an older term for post-traumatic stress disorder, is a common disorder of retired EMTs.
In a patient whose fracture has been splinted, no sensation is assessed on the area of injury. The nurse:
- Proceeds, as this is normal after splinting
- Immediately transfers the patient to the hospital
- Removes the splint and reapplies it
- Assesses again for sensation in 60 seconds
Rationalization
3
The loss of pulse, motor, or sensory response from a recently splinted extremity can be a result of a splint applied too tightly.
A patient is drowning on the beach. Which complication arises?
- Dehydration
- Edema
Rationalization
1
Drowning in saltwater will cause fluids to leave the body, producing dehydration.
What does MCI stand for?
- Any event that causes great damage and loss of life
- Any incident the exceeds the responder’s capability to treat and transport
Rationalization
2
An MCI stands for “Mass Casualty Incident”, where the number of patients exceed the amount of healthcare resources available. The definition in Option 1 is a disaster.
In an explosion, what vehicle is placed in front of the rescue convoy?
- Fire engine followed by the ambulance
- Ambulance followed by the fire engine
Rationalization
1
The fire engine is stronger, I guess
PTSD, previously known as operational exhaustion, happens to prehospital personnel because of:
- Too many failed attempts at CPR
- Too much love will kill you
- Too much time spent on service
- Too many injuries seen during responses
Rationalization
4
The amount of injury and death seen during responses, not only in CPR, is a precursor to post-traumatic stress disorder.
Patient is drowning in a river. The complication expected is:
- Edema
- Dehydration
Rationalization
1
Drowning in freshwater will result in edema formation.
Every liter of O₂ is equivalent to 4% FiO₂, the how many percent of oxygen is given if we administer 1 L/min. via cannula to the patient?
- 21%
- 25%
- 4%
Rationalization
2
Each liter of oxygen delivered per minute is equal to 4% FiO₂. Add this to the existing 21% of oxygen in the atmosphere to get the correct answer of 25%.
An EMT’s most important assessment skill to use is the use of his:
- Nose
- Ears
- Lips
- Eyes
Rationalization
4
The eyes are the EMT’s most important tools for assessing a situation and a victim.
In CPR, the rescuer becomes exhausted. The action to do is:
- Stop immediately
- Finish the five cycles and stop
Rationalization
1
No ratio
In a rape patient who wishes to take a bath, the nurse:
- Give the patient a bath
- Tell the patient that they should not bathe
- Accompanies the patient in the bath
Rationalization
2
Physical evidence must be collected from the person in a medicolegal case such as rape. The patient is advised against taking a bath.
Verapamil is given to patients with:
- Bradycardia
- Asystole
- Arrhythmia
- Tachycardia
Rationalization
4
Remember the two heart rate drugs: Atropine and Verapamil. Imagine the “A” in atropine as an upward arrow; a drug to increase heart rate, and the “V” in verapamil as a downward arrow; a drug to decrease heart rate.
In rescuing a patient who is drowning, the rescuer swims:
- From the front of the patient
- From the back of the patient
Rationalization
2
No ratio
The patient is receiving 15 L/min of O2 via a non-rebreather mask. What is the FiO2 being delivered?
- 91%
- 81%
- 21%
Rationalization
2
Each liter of oxygen delivered per minute is equal to 4% FiO₂. Add this to the existing 21% of oxygen in the atmosphere to get the correct answer of 81%.
During CPR, what accessory can hinder the rescuer from performing compressions?
- Ring
- Mask
- Watch
- Belt
Rationalization
3
The placement of the arms and hands on the breastbone may be obstructed with the presence of a watch.
In a person drowning in a pool, the priority is:
- Pulse
- Safety
- Airway
- Looking for other drowning persons
Rationalization
2
Safety is prioritized as the patient is actively drowning.
A patient who drowned is being managed. Which is appropriate?
- Compression only
- Mouth-to-mouth only
- Compressions and two mouth-to-mouth for five cycles
Rationalization
1
No mouth-to-mouth is done because this obstructs the effort to expel fluid from the patient’s lungs.
Before the term “ambulance”, they were called in war as:
- Moving clinics
- Mobile sanitariums
- Field hospitals
Rationalization
3
They were referred to as “field hospitals”.
In an unconscious patient who has been rescued from electrocution, the nurse:
- Performs CPR
- Avoids touching the patient
Rationalization
1
CPR can be performed as the patient has been rescued and is not a risk for electrocution to the nurse.
In a patient with a fractured femur, they are tagged in triage as:
- Red
- Black
- Green
- Yellow
Rationalization
1
The patient with a fractured femur is at risk for pulmonary embolism and massive bleeding. They are tagged red for immediate required care.
A patient is thirsty after electrocution. The nurse:
- Places them on NPO status
- Allows them to drink water
- Only allow ice chips
Rationalization
1
The patient who has been electrocuted is placed on NPO status
A pulseless patient with minimal wounds after electrocution:
- Ignore the wounds and perform CPR
- Treat the wounds then perform CPR
Rationalization
1
Minimal injuries means the rescuer can prioritize establishing circulation.
The Latin term “fercuium” in english refers to:
- Stretcher
- Carriage
- First aid
Rationalization
1
Fercuium refers to a frame; a stretcher.
which of the following is more dangerous?
- Liquefied petroleum gas and fire
- Gasoline and cigarettes
- Oxygen tank and fire
Rationalization
3
An oxygen tank and fire acts as if a grenade. 1 will ignite, but will appear as if a flamethrower. 2 is unlikely to ignite.
A child has ingested non-corrosive materials.
- Induce vomiting
- Do not induce vomiting
- Lay the client on their right side
- Place the client on Trendelenburg’s position
Rationalization
1
Patients who have ingested non-corrosive materials may vomit the material up to reduce absorption. This will minimally damage the esophagus. Clients are laid on their left side, and not on Trendelenburg’s position.
Which comes first in using a fire extinguisher?
- Swing
- Push
- Squeeze
- Aim
Rationalization
PASS: Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
An ambulance transporting a stable patient will have:
- Lights on
- Sirens on
- Lights and sirens on
Rationalization
1
No ratio